Tieto internetové stránky obsahujú informácie, ktoré sú určené výhradne odborníkom v zdravotníctve. Potvrdzujem, že som odborníkom v zdravotníctve.

Uľahčite si kontrolu glykémie u svojich pacientov s diabetom1-4
Špeciálna výživa pre pacientov s diabetom alebo hyperglykémiou – kontrola glykémie vďaka špecifickým sacharidom, proteínom, vyššiemu podielu energie v tukoch (MUFA) a obsahu vlákniny:
Kontrola glykémie je spojená s redukciou a progresiou rozvoja mikrovaskulárnych (napríklad retino/neuro/nefropatie), ale aj makrovaskulárnych komplikácii (napríklad ICHS).10,11
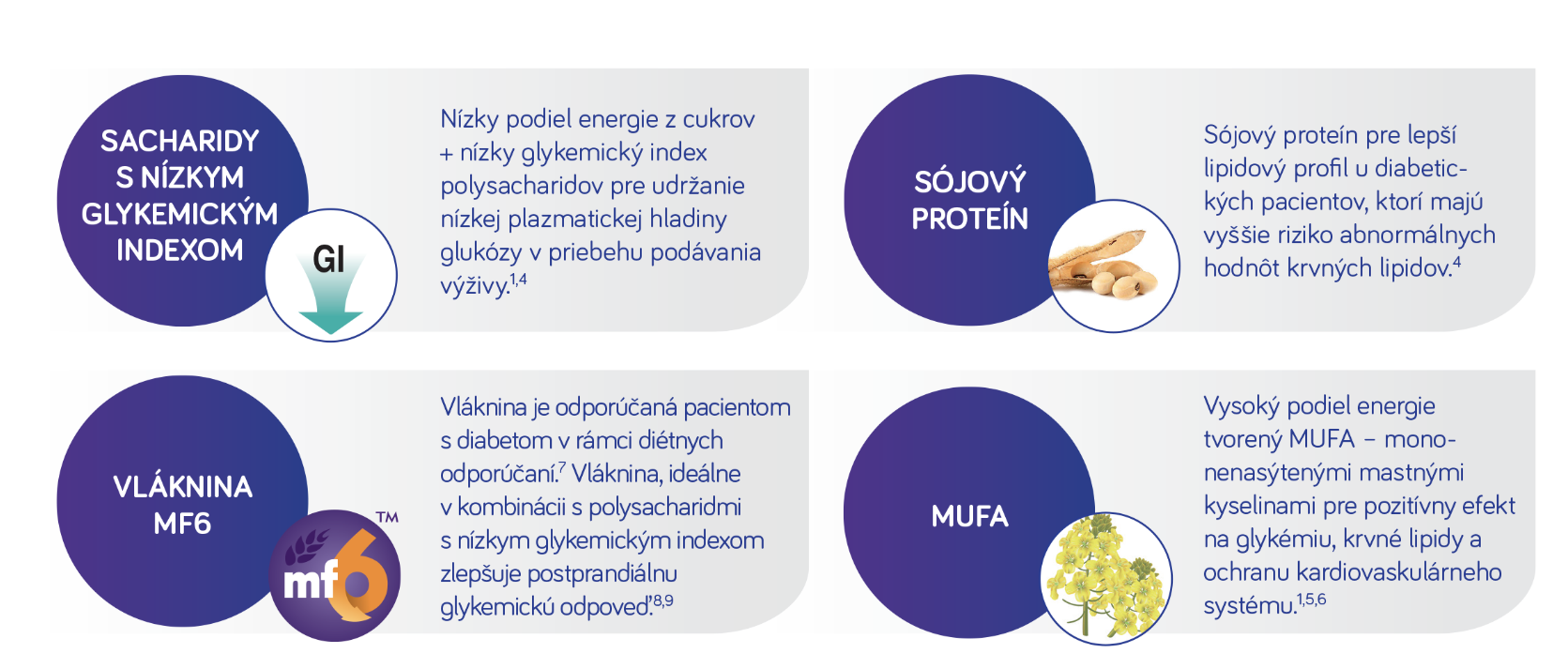
Nutrison Advanced Diason Energy HP
Hyperkalorická, vysokoproteínová výživa pre diabetikov so zvýšenou potrebou energie a proteínov4

Nutrison Advanced Diason Energy HP je indikovaný u pacientov s hyperglykémiou alebo diabetom4, ktorí
Pre pokrytie zvýšenej potreby energie a proteínov v priebehu metabolického stresu, s redukovaným objemom výživy alebo v rekonvalescencii
Preskripčné obmedzenie: INT, PED, DIA, GIT; L7 – množstvový limit: 2; L8 – množstvový limit: 5.
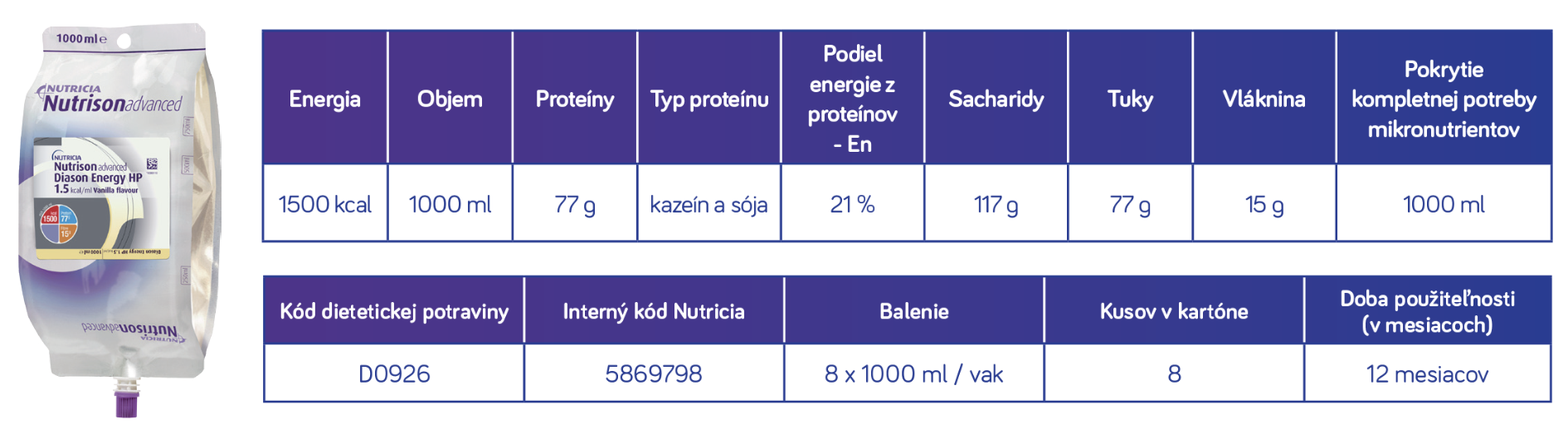
Nutrison Advanced Diason Low Energy
Nutrične kompletná hypokalorická výživa pre diabetikov s nízkou potrebou energie2

Pri administrácii výživy u svojich pacientov nezabúdajte na výživu čreva!
Využite unikátnu kompozíciu pre pokrytie potrieb trofickej výživy alebo u pacientov s nízkou potrebou energie
Nutrison Advanced Diason Low Energy:
Pri nízkej potrebe energie a živín, napr.: prechod z PV na EV, výživa sliznice čreva, imobilní krehkí seniori, pacienti pripútaní na lôžko, obézni alebo pacienti s nízkokalorickou diétou
PDF NA STIAHNUTIE NÁJDETE NA KONCI ČLÁNKU
Referencie:
1. Sanz-Paríz A, Matía-Martín P, Martín-Palermo Á, et al. Diabetes-specific Formulas High in Monounsaturated Fatty Acids and Metabolic Outcomes in Patients With Diabetes or Hyperglycaemia. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Nutr . 2020 Mar 16; S0261-5614(20)30100-X.
2. Elia M, Ceriello A, Laube H, et al. Enteral Nutritional Support and Use of Diabetes-Specific Formulas for Patients With Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Care. 2005 Sep; 28(9):2267-2279.
3. Vaisman N, Lansink M, Rouws CH, et al. Tube feeding with a diabetes-specific feed for 12 weeks improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. Clin Nutr. 2009; 28:549e55.
4. Lansink M, Hofman Z, Genovese S, et al. Improved glucose profile in patients with type 2 diabetes with a new, high-protein, diabetes-specific tube feed during 4 hours of continuous feeding. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2017; 41:968e75.
5. Mensink RP, Zock PL, Kester ADM, Katan MB. Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and apolipoproteins: a meta-analysis of 60 controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003; 77:1146–1155.
6. Schwingshackl L, Hoffmann G. Monounsaturated fatty acids and risk of cardiovascular disease: synopsis of the evidence available from systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Nutrients. 2012; 4:1989–2007.
7. Adler A. IDF Clinical Practice Recommendations for managing Type 2 Diabetes in Primary Care, 2017. Retrieved from: https://www.idf.org/component/attachments/attachments.html?id=1585&task=download. [17.7.2020]
8. Laksir H, Lansink M, Reguemme SC, et al. Glycaemic Response After Intake of a High Energy, High Protein, Diabetes-Specific Formula in Older Malnourished or at Risk of Malnutrition Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Clin Nutr. 2018 Dec; 37(6 Pt A):2084-2090.
9. Lightowler H, Thondre S, Holz A, et al. Replacement of Glycaemic Carbohydrates by Inulin-Type Fructans From Chicory (Oligofructose, Inulin) Reduces the Postprandial Blood Glucose and Insulin Response to Foods: Report of Two Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trials. Eur J Nutr. 2018 Apr; 57(3):1259-1268.
10. Cosentino F, Grant PJ , Aboyans V, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines on Diabetes, Pre-Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases Developed in Collaboration With the EASD. Eur Heart J. 2020 Jan 7; 41(2):255-323.
11. Riddle MC. Ed. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes - 2020. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43(S1):S1-S212.
12. McClave SA, Taylor BE, Martindale RG, et al. Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Adult Critically Ill Patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016 Feb; 40(2):159-211.
13. Singer P, Blaser AR, Berger MM, et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in the intensive care unit. Clin Nutr. 2019 Feb; 38(1):48-79.
14. Zhang D, Li H, Li Y, et al. Gut rest strategy and trophic feeding in the acute phase of critical illness with acute gastrointestinal injury. Nutr Res Rev. 2019 Dec; 32(2):176-182.
15. Rice TW, Wheeler AP, Thompson BT, et al. Initial trophic vs full enteral feeding in patients with acute lung injury: the EDEN randomized trial. JAMA. 2012 Feb 22; 307(8):795-803.
16. Heyland DK. Safety of Prolonged Use of Trophic Feeds in the Critically Ill Patient: It Depends on the Nutrition Risk of the Patient! JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2016 May; 40(4):452-454.
17. Freemont RD, Rice TW. How soon should we start interventional feeding in the ICU? Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2014 Mar; 30(2):178-181.
18. Rice TW, Mogan S, Hays MA, et al. Randomized trial of initial trophic versus full-energy enteral nutrition in mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory failure Crit Care Med. 2011 May; 39(5):967–974.
PDF | Leták Nutrison Advanced Diason | 14.32 MB |
 Odber noviniek
Odber noviniek
Zde máte možnost přizpůsobit soubory cookie podle kategorií, v souladu s vlastními preferencemi.

Jedná se o technické soubory, které jsou nezbytné ke správnému chování našich webových stránek a všech jejich funkcí. Používají se mimo jiné k ukládání produktů v nákupním košíku, zobrazování produktů na přání, ovládání filtrů, osobního nastavení a také nastavení souhlasu s uživáním cookies. Pro tyto cookies není zapotřebí Váš souhlas a není možné jej ani odebrat.

Tyto cookies nám umožňují měřit výkonnost našich webových stránek a našich online kampaní. S jejich pomocí zjišťujeme počet návštěv, zdroj návštěv a další parametry. Shromážděné údaje zjišťujeme v agregované podobě, která nám neumožňuje údaje dohledat ke konkrétnímu uživateli. Pokud tyto cookies deaktivujete, nebudeme moci analyzovat výkonnost našich webových stránek a optimalizovat je pro co nejsnažší užívání.

Tyto cookies nám umožňují lépe cílit a vyhodnocovat marketingové kampaně.
